
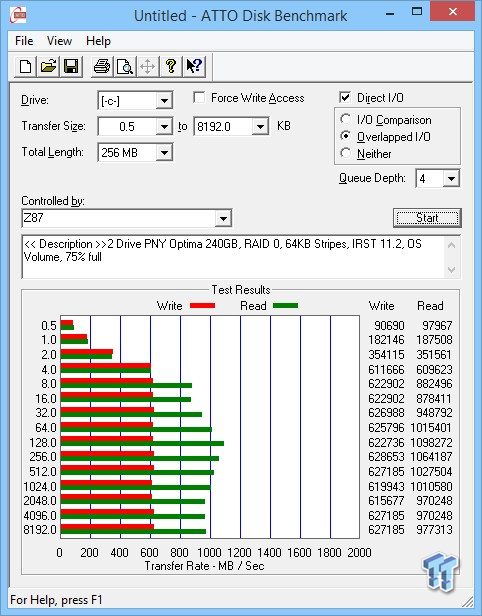
When only small amounts are erased, the storage capacity is reduced. The NAND gate-style allows a user to program or read the data one byte or word at a time, but erases data in blocks. Typically, the device can go through 100,000 P/E cycles before the integrity of the unit is compromised and files become corrupted.Īnother limitation concerns the way manufacturers build the devices. Each drive has a limited number of program-erase cycles (P/E cycles), which is the act of putting files onto the drive and erasing them. Pen drives do have a few limitations, including how many times they can be used. There are also programs that can be run directly from the drive, without needing to be installed on the computer first. Any file that can be stored on a computer's hard drive can usually be copied to a flash drive, as long as there is enough memory. Depending on the storage size, flash drives can hold anywhere from 128 MB to 32 GB or more by comparison, a standard CD-ROM holds about 700 MB of data.Įven a pen drive with a relatively low storage capacity tends to provide plenty of space for all different types of files. Because they are solid state - there are no moving parts - flash drives usually last longer and the data stored on them is safer. They can transfer data much more quickly than these older technologies.
BenefitsĮquipped with a large amount of memory, the pen drive is often considered to be an improvement on both the older floppy drive disks and the more modern compact disks. The age of the drive and how it's being used - such as for writing and erasing small files - also affects the transfer speed. Manufacturers usually list the speed in megabytes per second (MB/s). Generally, a pen drive's advertised speed is the reading speed because it is faster than the speed at which data can be written to it. The actual transfer speed depends upon several factors, such as the computer's speed at reading and writing to the device. Using blocks rather than allowing random access allows the drive to store more information and be made at a lower cost. This technology works by storing data in blocks rather than randomly as such, it doesn't work in the same way that a computer's main memory systems - read-only memory (ROM) and random-access memory (RAM) - do. Technicians classify pen drives as NOT AND, also called NAND, gate-style data storage devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
